
MACROLIDES Erythromycin Clarithromycin Azithromycin Mechanism of action Inhibit protein synthesis by binding to the 50 s subunit Antibacterial activity. - ppt download
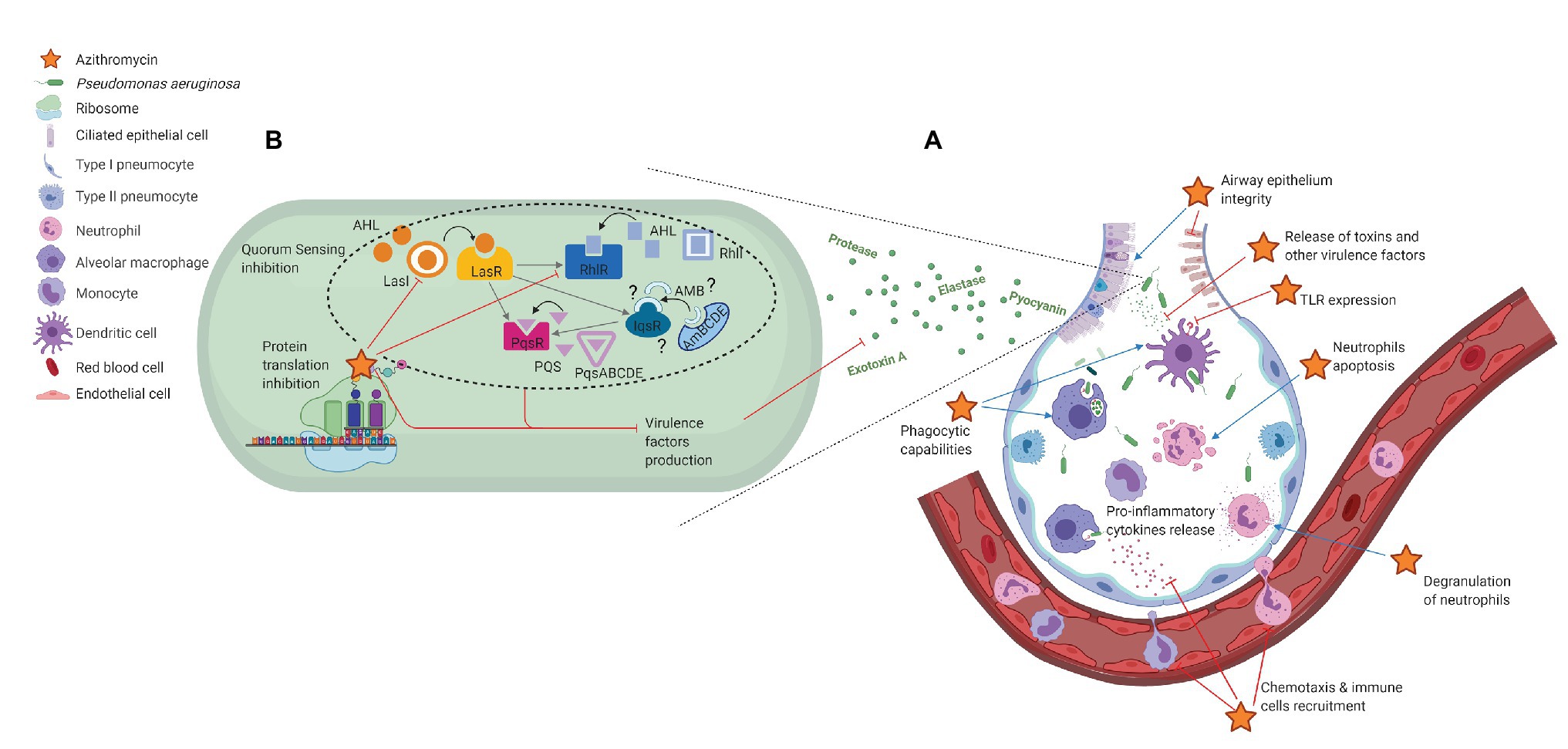
Frontiers | Could Azithromycin Be Part of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Acute Pneumonia Treatment? | Microbiology

Mechanisms of Action and Clinical Application of Macrolides as Immunomodulatory Medications | Clinical Microbiology Reviews
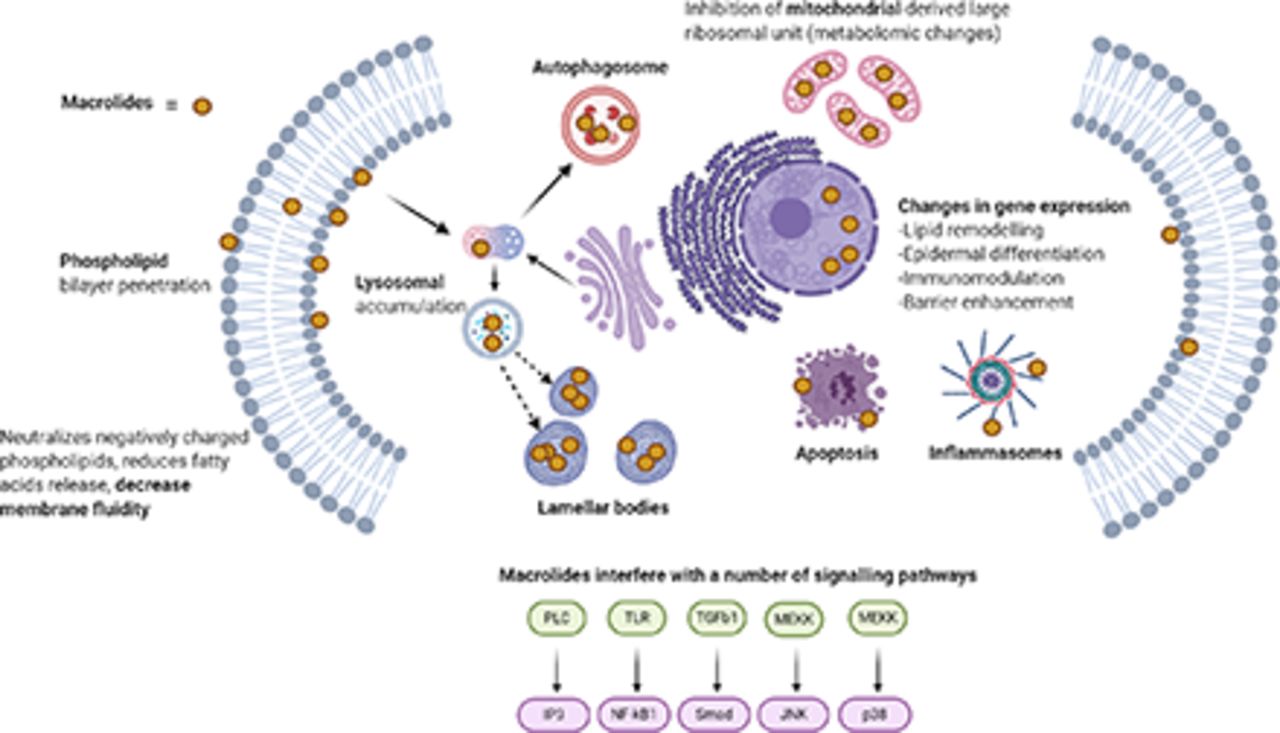
Nonantimicrobial Actions of Macrolides: Overview and Perspectives for Future Development | Pharmacological Reviews

Rationale for azithromycin in COVID-19: an overview of existing evidence | BMJ Open Respiratory Research

البورد العراقي للصيدلة السريرية - 📣Azithromycin (Zithromax) 💡Mechanism of action Binds with ribosomal receptor sites in susceptible organisms to inhibit bacterial protein synthesis; is a derivative of erythromycin. 🛑USES ✓Treats respiratory, ear,

Immunomodulation by macrolides: therapeutic potential for critical care - The Lancet Respiratory Medicine
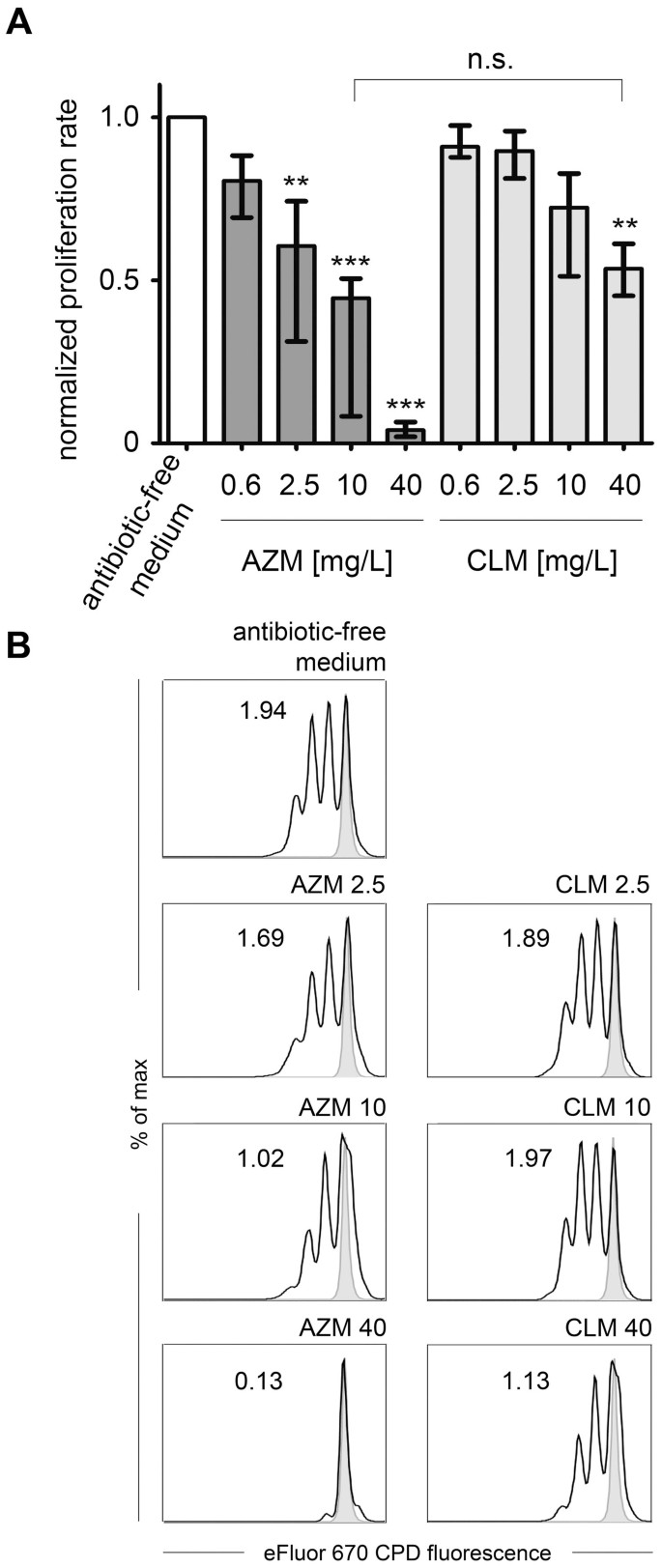
Azithromycin suppresses CD4+ T-cell activation by direct modulation of mTOR activity | Scientific Reports
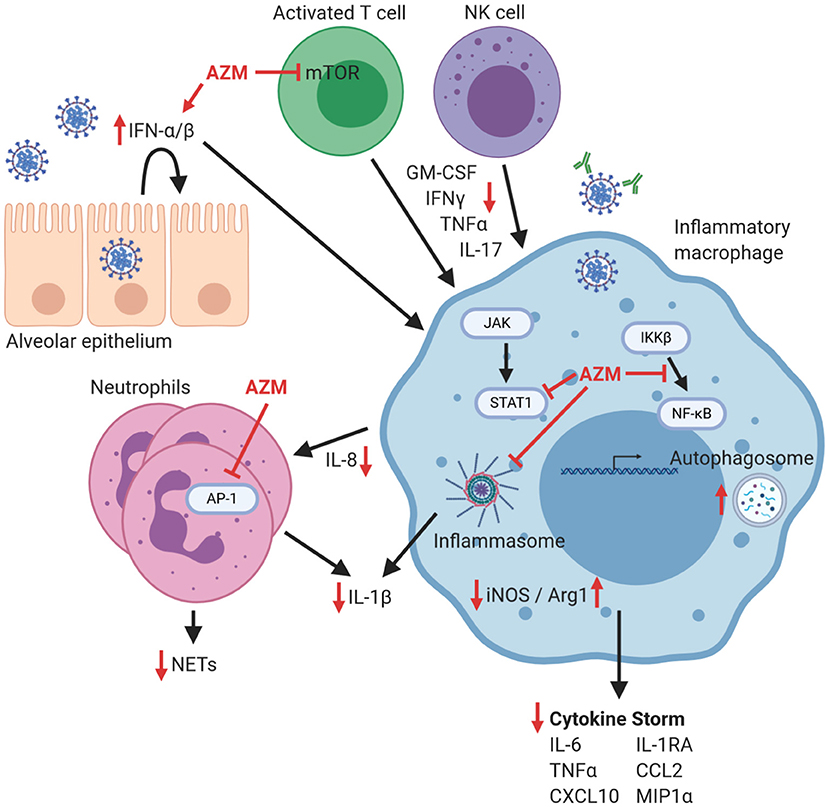
Frontiers | Immunomodulatory Effects of Azithromycin Revisited: Potential Applications to COVID-19 | Immunology

Azithromycin: mechanisms of action and their relevance for clinical applications. | Semantic Scholar
What is the evidence for using macrolide antibiotics to treat COVID-19? - The Centre for Evidence-Based Medicine
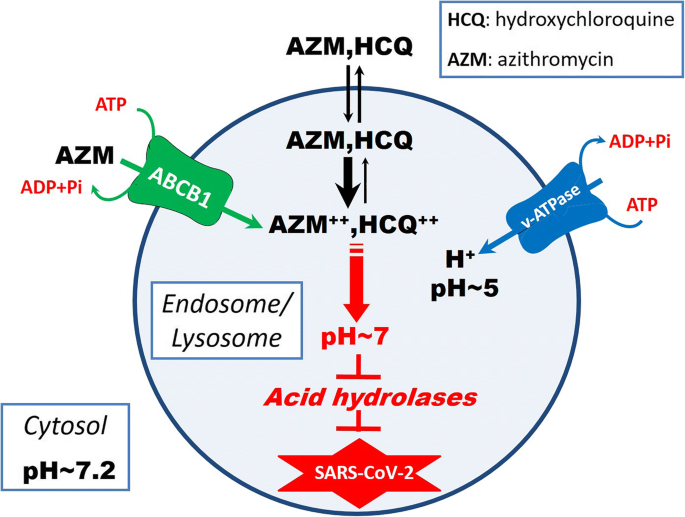
Intracellular ABCB1 as a Possible Mechanism to Explain the Synergistic Effect of Hydroxychloroquine-Azithromycin Combination in COVID-19 Therapy | SpringerLink



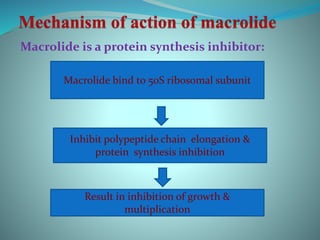
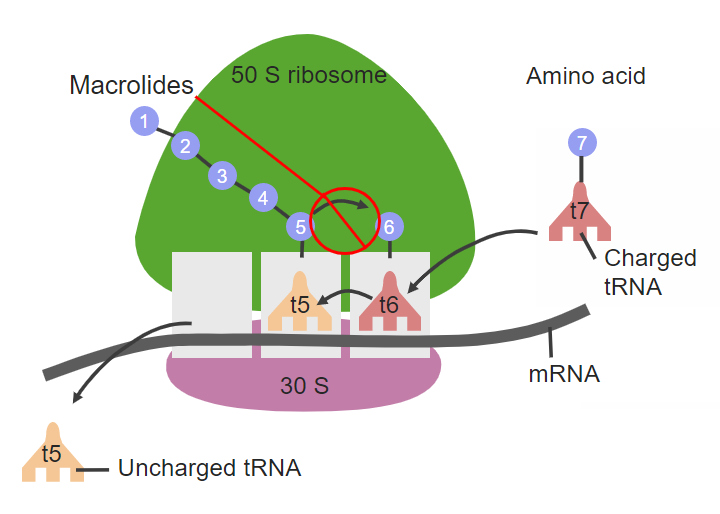

![macrolides [TUSOM | Pharmwiki] macrolides [TUSOM | Pharmwiki]](https://tmedweb.tulane.edu/pharmwiki/lib/exe/fetch.php/macrolides2.png?w=600&tok=23fb00)





